Submarine Optical Fiber Cable: Backbone of Global Digital Connectivity
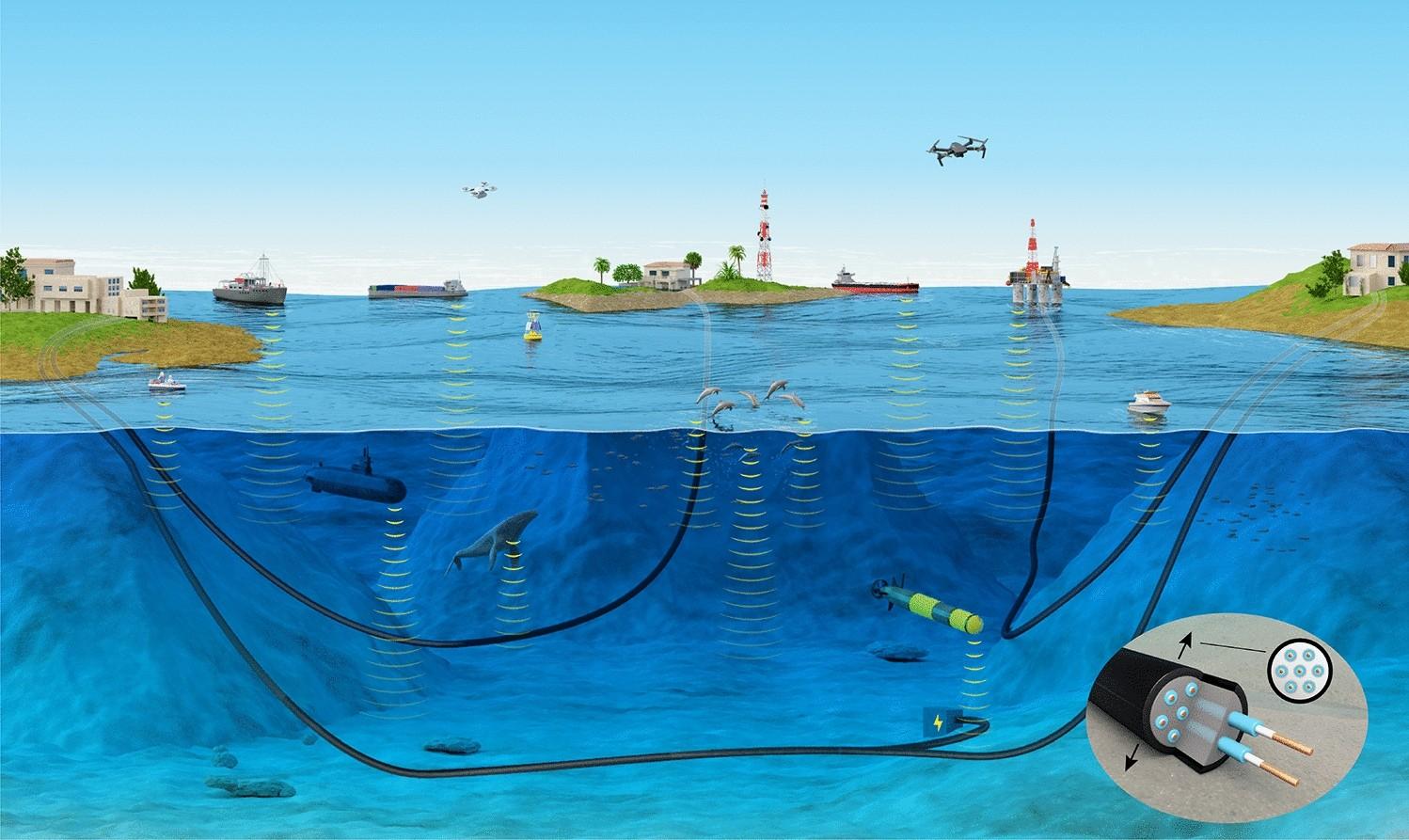
Submarine optical fiber cables form the invisible backbone of the modern digital world, enabling high-speed communication across continents and oceans. These cables, laid on the seabed, carry more than 95% of international data traffic, including internet services, cloud computing, financial transactions, and real-time communications. By using optical fibers that transmit data as pulses of light, submarine cables offer unmatched bandwidth, low latency, and high reliability compared to satellite-based communication systems.
Source -
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/submarine-optical-fiber-cable-market-22287
The basic structure of a submarine optical fiber cable is designed to withstand extreme underwater conditions. At its core are optical fibers made of ultra-pure glass, surrounded by protective layers such as gel compounds, plastic insulation, steel wire armoring, and waterproof sheathing. Near coastal areas, where risks from fishing activities, anchors, and shallow waters are higher, cables are heavily armored. In deeper ocean regions, lighter designs are used to balance durability and cost efficiency while maintaining performance.
The deployment of submarine optical fiber cables is a highly specialized and complex process. Detailed seabed surveys are conducted to identify safe routes that avoid geological hazards such as earthquakes, underwater volcanoes, and steep slopes. Cable-laying ships then carefully place the cable along the planned route, sometimes burying it beneath the seabed near shorelines for additional protection. Once installed, these cables are monitored continuously, and repair ships are dispatched promptly in case of faults to minimize service disruptions.
Submarine optical fiber cables play a critical role in supporting global economic growth and digital transformation. They enable seamless international trade, support global financial markets, and facilitate cross-border collaboration in sectors such as healthcare, education, research, and entertainment. With the rapid growth of cloud services, video streaming, artificial intelligence, and data-intensive applications, demand for higher-capacity submarine cable systems continues to rise, driving ongoing investments in new routes and advanced technologies.
Technological advancements have significantly improved the performance and efficiency of submarine optical fiber cables. Innovations such as dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) allow multiple data channels to be transmitted simultaneously over a single fiber, dramatically increasing capacity. Improved optical amplifiers and repeaters extend transmission distances while maintaining signal quality, reducing the need for frequent regeneration and lowering operational costs over the cable’s lifespan.
Despite their advantages, submarine optical fiber cables face challenges related to security, maintenance, and environmental impact. Accidental damage from human activities and natural events remains a concern, while geopolitical considerations and data security issues are gaining importance as global dependence on these networks grows. Nevertheless, continued innovation, international cooperation, and robust regulatory frameworks are strengthening the resilience of submarine cable infrastructure.
Submarine optical fiber cables are essential to the functioning of the global digital ecosystem. As the demand for fast, reliable, and high-capacity connectivity continues to expand, these undersea networks will remain a foundational element of global communication, supporting economic development, technological progress, and digital inclusion worldwide.
Submarine Optical Fiber Cable: Backbone of Global Digital Connectivity
Submarine optical fiber cables form the invisible backbone of the modern digital world, enabling high-speed communication across continents and oceans. These cables, laid on the seabed, carry more than 95% of international data traffic, including internet services, cloud computing, financial transactions, and real-time communications. By using optical fibers that transmit data as pulses of light, submarine cables offer unmatched bandwidth, low latency, and high reliability compared to satellite-based communication systems.
Source - https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/submarine-optical-fiber-cable-market-22287
The basic structure of a submarine optical fiber cable is designed to withstand extreme underwater conditions. At its core are optical fibers made of ultra-pure glass, surrounded by protective layers such as gel compounds, plastic insulation, steel wire armoring, and waterproof sheathing. Near coastal areas, where risks from fishing activities, anchors, and shallow waters are higher, cables are heavily armored. In deeper ocean regions, lighter designs are used to balance durability and cost efficiency while maintaining performance.
The deployment of submarine optical fiber cables is a highly specialized and complex process. Detailed seabed surveys are conducted to identify safe routes that avoid geological hazards such as earthquakes, underwater volcanoes, and steep slopes. Cable-laying ships then carefully place the cable along the planned route, sometimes burying it beneath the seabed near shorelines for additional protection. Once installed, these cables are monitored continuously, and repair ships are dispatched promptly in case of faults to minimize service disruptions.
Submarine optical fiber cables play a critical role in supporting global economic growth and digital transformation. They enable seamless international trade, support global financial markets, and facilitate cross-border collaboration in sectors such as healthcare, education, research, and entertainment. With the rapid growth of cloud services, video streaming, artificial intelligence, and data-intensive applications, demand for higher-capacity submarine cable systems continues to rise, driving ongoing investments in new routes and advanced technologies.
Technological advancements have significantly improved the performance and efficiency of submarine optical fiber cables. Innovations such as dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) allow multiple data channels to be transmitted simultaneously over a single fiber, dramatically increasing capacity. Improved optical amplifiers and repeaters extend transmission distances while maintaining signal quality, reducing the need for frequent regeneration and lowering operational costs over the cable’s lifespan.
Despite their advantages, submarine optical fiber cables face challenges related to security, maintenance, and environmental impact. Accidental damage from human activities and natural events remains a concern, while geopolitical considerations and data security issues are gaining importance as global dependence on these networks grows. Nevertheless, continued innovation, international cooperation, and robust regulatory frameworks are strengthening the resilience of submarine cable infrastructure.
Submarine optical fiber cables are essential to the functioning of the global digital ecosystem. As the demand for fast, reliable, and high-capacity connectivity continues to expand, these undersea networks will remain a foundational element of global communication, supporting economic development, technological progress, and digital inclusion worldwide.
·89 Views
·0 previzualizare